Blockchain in Land Registries
Learn how blockchain is transforming land registries in Kenya. Discover benefits, real-world use cases, fraud prevention, and how to implement a blockchain-based land registry system.
Introduction
Blockchain in Land Registries
Land ownership in Kenya and many other countries still faces problems like fraud, missing records, and slow property transfers. These issues make buying or investing in land risky and stressful for many people.
Blockchain In Land Registries offers a modern solution by storing land records on secure, decentralized systems. This approach improves transparency, supports blockchain title deed verification, and helps create safer property transactions for buyers, governments, and investors.
What Is Blockchain in Land Registries?
Definition of Blockchain In Land Registries
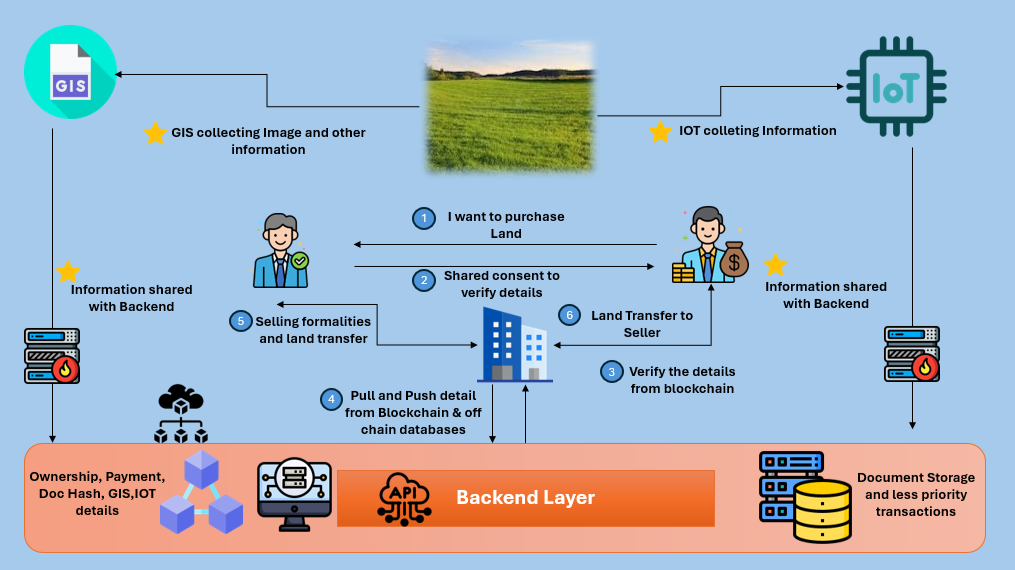
Blockchain In Land Registries refers to the use of blockchain technology to store, verify, and manage land ownership records in a secure digital format. Instead of relying on centralized databases, property information is distributed across multiple nodes, making it tamper-resistant and transparent. This approach supports blockchain based land registry systems that help reduce fraud while improving trust in property transactions.
How a Land Registry Using Block Chain Works
A land registry using block chain records every property transaction as a permanent digital entry on a decentralized network. Each change in ownership is verified by multiple participants before being added, ensuring accuracy and preventing unauthorized edits. This creates decentralized land registry solutions where buyers can confirm ownership history in real time.
Key Components of a Blockchain Based Land Registry
A blockchain based land registry typically includes smart contracts, digital identities, encrypted title records, and distributed storage. Smart contracts automate land transfers once conditions are met, while digital IDs confirm the identity of buyers and sellers. Together, these elements power secure blockchain title deed verification and faster property settlements.
Difference Between Traditional vs Blockchain Land Registry Systems
Traditional registries depend on manual processes and centralized databases, which are vulnerable to errors and manipulation. Blockchain systems use immutable digital records that cannot be altered without network approval, making ownership data more reliable. This shift toward digital property ownership systems improves transparency and reduces disputes.

Problems With Traditional Land Registry Systems
Land Fraud, Double Allocation, and Fake Title Deeds
Land fraud remains one of the biggest risks in property transactions, with cases of duplicate allocations and forged title deeds affecting many buyers. These issues arise from weak verification systems and fragmented records. Blockchain land registry systems help address this by creating a single trusted source of ownership data.
Manual Records, Missing Files, and Human Error
Many land offices still rely on paper files and outdated databases, leading to misplaced documents and inconsistent records. Human error during data entry also causes ownership conflicts and delays. Digitization combined with blockchain creates Kenya blockchain land records that are easier to manage and audit.
Slow Transfers and High Transaction Costs
Property transfers can take months due to lengthy approvals, physical file movement, and multiple intermediaries. These delays increase costs for buyers and discourage investment. Smart contracts for land transactions help automate approvals and significantly shorten transfer timelines.
Lack of Transparency for Buyers and Investors
Buyers often struggle to confirm true ownership or transaction history before purchasing land. This lack of visibility creates uncertainty and raises the risk of financial loss. Blockchain provides open verification tools that support blockchain property ownership security for both local and diaspora investors.
How Blockchain Technology Enables Secure Land Records
Decentralization and Immutable Property Data
Blockchain stores land records across multiple nodes instead of one central server, reducing the risk of data loss or manipulation. Once information is recorded, it cannot be changed without network consensus. This immutability is a core benefit of decentralized land registry solutions.
Smart Contracts for Automated Land Transactions
Smart contracts automatically execute land transfers once agreed conditions are fulfilled, such as payment confirmation. This removes middlemen, speeds up settlements, and lowers administrative costs. Smart contracts for land transactions also improve accuracy by eliminating manual intervention.
Digital Identity and Title Verification on Blockchain
Blockchain integrates digital identity systems to confirm the legitimacy of buyers, sellers, and property owners. This ensures only authorized parties can initiate transfers while supporting blockchain title deed verification. It also strengthens trust across digital property ownership systems.
Audit Trails and Real-Time Ownership Tracking
Every transaction on a blockchain creates a permanent audit trail that can be reviewed at any time. Buyers and authorities can track ownership changes in real time, improving accountability and transparency. This feature is especially valuable for blockchain and land registries in Kenya, where historical data is often hard to access.
Blockchain and Land Registries in Kenya
Current State of Kenya’s Land Registry Digitization
Kenya has made significant progress in digitizing land records through initiatives like the ArdhiSasa platform, which allows citizens to access and verify property information online. Despite this progress, many records are still incomplete or scattered across different offices, creating challenges for accurate verification. Implementing blockchain and land registries in Kenya could unify these records into a single secure platform, reducing fraud and improving trust for buyers and investors.
Blockchain and Land Registries in Kenya PDF Resources
Several reports and guides are now available in PDF format to help stakeholders understand how blockchain can improve land registry systems in Kenya. These resources provide step-by-step frameworks, case studies, and best practices for implementing a blockchain based land registry. Accessing these PDF guides allows investors, policymakers, and developers to make informed decisions on adopting blockchain technology.
Legal, Policy, and Infrastructure Readiness in Kenya
Adopting blockchain for land registries requires a supportive legal framework, clear property laws, and reliable digital infrastructure. Kenya’s current land laws are evolving to accommodate digital ownership verification, but gaps remain in policy clarity and data standardization. Addressing these challenges is critical to ensure that land registry using block chain is legally recognized and operationally effective.

Global Blockchain Based Land Registry Models
Case Studies From Sweden, Georgia, and Dubai
Countries like Sweden, Georgia, and Dubai have successfully implemented blockchain in their land registry systems, demonstrating faster transactions, reduced fraud, and improved transparency. These models highlight the advantages of using decentralized ledgers and smart contracts for property management. Kenya can draw lessons from these international examples when designing its own blockchain land registry system.
Lessons Kenya Can Learn From Global Adoption
Global adoption shows that combining digitization with blockchain improves trust and efficiency in property transactions. Key lessons include the need for clean digital data, regulatory alignment, and user training for smooth implementation. Applying these strategies can help Kenya implement blockchain and land registries in Kenya successfully.
Why Clean Digital Records Must Come Before Blockchain
Blockchain is only as effective as the data it holds, so having complete and accurate digital land records is essential. Attempting to implement blockchain without first cleansing and standardizing records may replicate existing errors and fraud. Preparing data in advance ensures that blockchain based land registry solutions deliver reliable and verifiable property ownership.
How to Implement a Blockchain Land Registry System
echnical Requirements for a Blockchain Land Registry Platform
Implementing a blockchain land registry requires secure servers, distributed ledger technology, smart contract frameworks, and identity verification tools. The system must be scalable to handle all property records while maintaining fast transaction processing. Meeting these technical requirements for a blockchain land registry platform ensures the solution is secure, reliable, and sustainable.
Integration With Government and Existing Land Databases
A successful blockchain land registry must integrate seamlessly with existing government databases, legal registries, and digital platforms. This ensures consistency between traditional records and blockchain entries while enabling real-time verification of property ownership. Integration also allows smooth transition from manual systems to land registry using block chain without disrupting services.
Cost, Timeline, and ROI for Blockchain In Land Registries
The cost of implementing a blockchain land registry varies based on the number of properties, digital infrastructure, and regulatory requirements. While initial investment can be significant, the long-term benefits include reduced fraud, faster transactions, and lower administrative costs. Calculating ROI helps governments and investors understand the financial and operational advantages of blockchain in land registries.

Conclusion
Summary of Key Benefits and Use Cases
Blockchain In Land Registries ensures secure, transparent, and efficient property ownership. It reduces fraud, accelerates land transfers, and builds trust among buyers, governments, and investors.
This technology is especially valuable in Kenya, where digital land records are still developing. Blockchain adoption can transform the property sector, creating reliable and accessible land ownership systems for all stakeholders.
Why Blockchain In Land Registries Is Inevitable for Secure Property Ownership
As global examples show, blockchain improves accountability and streamlines property transactions. Its ability to store immutable, verifiable ownership data makes it essential for modern land registry systems. Governments and investors worldwide are recognizing its importance.
Kenya’s Opportunity to Lead Africa in Blockchain Land Systems
Kenya can become a pioneer in African blockchain land registry adoption by combining digitization, policy reforms, and modern infrastructure. Early adoption can position the country as a regional leader in secure digital property management.