How Inflation Impacts Property Prices in Kenya
Explore how inflation is influencing property prices in Kenya in 2025. Understand the factors driving changes in real estate values and discover strategic insights for buyers and investors.
Introduction
In 2025, Kenya’s property market is evolving rapidly, and inflation is a key factor influencing housing prices across the country. Understanding how inflation and property prices in Kenya interact helps investors and buyers make informed decisions. With the economy facing rising costs in multiple sectors, knowing market trends can safeguard investments and guide purchasing strategies.
Understanding Inflation in Kenya
Inflation directly affects the affordability and demand for housing. Knowing the factors driving Kenya’s inflation helps buyers, investors, and developers anticipate changes in property prices and plan accordingly.
Current Inflation Trends
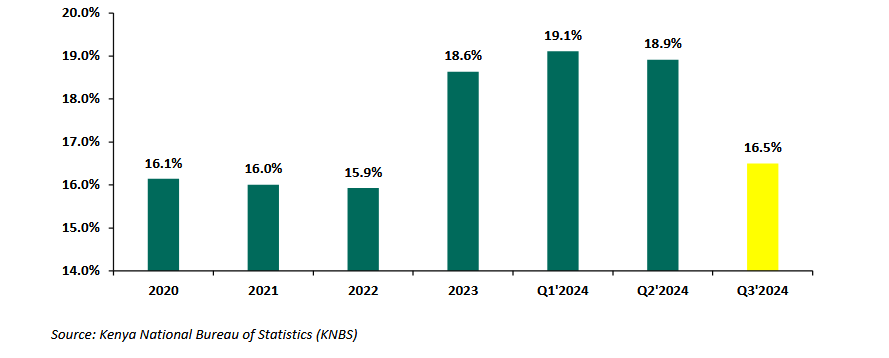
As of September 2025, Kenya’s annual inflation rate is 4.6%, slightly higher than the previous month. Key drivers include rising food and transport costs, increased housing expenses, and global commodity price fluctuations. The Central Bank of Kenya has adjusted the benchmark lending rate to 9.25% to stabilise the economy while supporting growth.
Factors Driving Inflation
Several factors contribute to inflation in Kenya:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply constraints have increased import costs.
- Rising Fuel Prices: Higher fuel costs impact transportation and construction expenses.
- Currency Depreciation: A weaker Kenyan Shilling makes imports more expensive.
- Demand Pressures: Economic recovery post-pandemic has increased demand for goods and services, including housing.
Inflation’s Impact on Consumer Behavior
Inflation affects how people spend and borrow:
- Reduced Disposable Income: Consumers have less money for non-essential purchases.
- Shift in Spending Priorities: Essentials are prioritised over luxury goods.
- Higher borrowing costs: Loans, including mortgages, become more expensive.
The Impact of Inflation on Property Prices
How Inflation Impacts Property Prices in Kenya
Inflation influences property prices in multiple ways, affecting both buyers and investors. Historical and current trends provide insight into what the future may hold.
Historical Perspective
Historically, periods of high inflation in Kenya coincided with notable increases in property prices. During the early 2000s, rapid inflation pushed construction costs higher, driving residential and commercial property values up. However, these periods often saw corrections afterward, showing that property prices respond dynamically to economic conditions.
Current Market Dynamics
In 2025, property prices in Kenya have risen by approximately 7.8%, outpacing inflation slightly. Contributing factors include:
- High Demand: Urbanisation and population growth increase housing needs.
- Investment inflows: Both local and foreign investors are boosting the market.
- Limited Supply: High construction costs and regulatory delays restrict new developments.
Regional Variations

Property price trends differ by region:
- Nairobi: Prices grow steadily in high-demand areas like Kilimani and Westlands.
- Coastal Areas: Mombasa sees seasonal fluctuations influenced by tourism.
- Rural Counties: Places like Kiambu and Machakos are emerging as attractive investment hubs due to affordability and proximity to Nairobi.
Sector-Specific Impacts
Different real estate sectors respond differently to inflation:
- Residential Properties: Generally see steady appreciation during inflationary periods.
- Commercial Properties: Office and retail spaces may experience slower growth due to higher operating costs.
- Land Investments: Undeveloped land often appreciates steadily, making it a safe hedge against inflation.
Real Estate Inflation in Kenya
Real estate inflation is the rate at which property prices increase, reflecting market demand, construction costs, and economic conditions. Tracking this helps investors and buyers make informed decisions.
Definition and Significance
Real estate inflation represents price growth in property over time. In Kenya, monitoring this metric is essential for evaluating potential returns on investment and predicting future market trends.
Key Indicators
Important metrics for real estate inflation include:
- Property Price Index: Measures average price changes across regions.
- Rental Yields: Indicates the return on rental investments.
- Construction Costs: Rising costs often lead to higher property prices.
Future Projections
Experts forecast moderate growth in real estate prices, influenced by:
- Economic Policies: Government measures to control inflation and stimulate growth.
- Global Economic Conditions: Trade and investment flows impact local real estate.
- Infrastructure Development: New roads, utilities, and urban expansion drive property value increases.
Housing Prices in Kenya: Current Trends
Kenya’s housing prices reflect the interplay between inflation, demand, and policy initiatives. Understanding these trends helps buyers and investors identify opportunities.
Urban vs. Rural Areas
Urban areas like Nairobi and Mombasa experience higher price growth due to limited space and high demand. Rural areas, however, offer affordable options for first-time buyers and investors seeking lower entry costs. Satellite towns like Athi River and Thika are seeing significant appreciation, offering value for early investors.
Affordable Housing Initiatives
The government has implemented measures to promote affordable housing:
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Collaboration with private developers to build low-cost units.
- Subsidised Loans: Financial products making homeownership accessible.
- Regulatory Reforms: Streamlining approvals to encourage more construction.
Investment Opportunities
Despite inflationary pressures, several property segments remain lucrative:
- Middle-Income Housing: High demand in satellite towns offers strong growth potential.
- Commercial Properties: Offices and retail spaces in urban areas attract investors.
- Land Investments: Emerging counties provide opportunities for long-term capital appreciation.
Impact of Inflation on Housing Affordability
Inflation raises the cost of building materials, labour, and land, making homes less affordable. Buyers may need to adjust their budgets or consider alternative locations to find value for money.
Navigating the Market: Tips for Buyers and Investors
Understanding inflation and property price dynamics helps buyers and investors make sound decisions.
Strategies for Buyers
- Research Market Trends: Track property prices, rental yields, and inflation rates.
- Consider Long-Term Value: Focus on areas likely to appreciate in value.
- Evaluate Financing Options: Compare mortgage rates to secure favorable terms.
Investment Considerations
- Diversify Portfolio: Spread investments across property types and regions.
- Assess Risk Factors: Consider economic and political conditions affecting property markets.
- Monitor Regulatory Changes: Stay informed about new policies affecting real estate.
Risk Management
- Conduct Due Diligence: Verify titles and ownership.
- Engage Professionals: Use real estate agents, lawyers, and financial advisors.
- Plan for Contingencies: Maintain reserves for unexpected costs or market downturns.
Leveraging Financing Options
- Fixed-Rate Mortgages: Protect against rising interest rates.
- Government Subsidies: Explore programs that reduce homeownership costs.
- Private Loans: Consider flexible terms for strategic investments.
Conclusion
Inflation significantly influences property prices in Kenya, affecting affordability, investment potential, and market stability. Understanding the relationship between inflation and property prices in Kenya allows buyers and investors to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on growth opportunities. Monitoring inflation trends, sector-specific price movements, and government initiatives is key to navigating the 2025 property market successfully.